What Causes the Four Seasons?
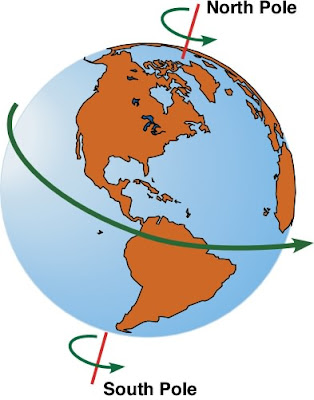
The four seasons are caused by the way the earth spins on it's axis. The tilt is the cause some areas of the earth will receive more sunlight than others.
Why do We have Four Seasons?
We have different seasons because the Earth rotates on its axis. As the Earth turns it gets closer to the sun at times. Then as it keeps going it gets further away from the sun. That’s what makes the seasons change.
What are the Four Seasons of the Year?
The four seasons of the year are Fall, Winter, Spring and Summer. Summer tends to be the hottest; winter is the coldest. Spring has nice warm temperatures and Fall has those temperatures that are just beginning to cool down.

.gif)